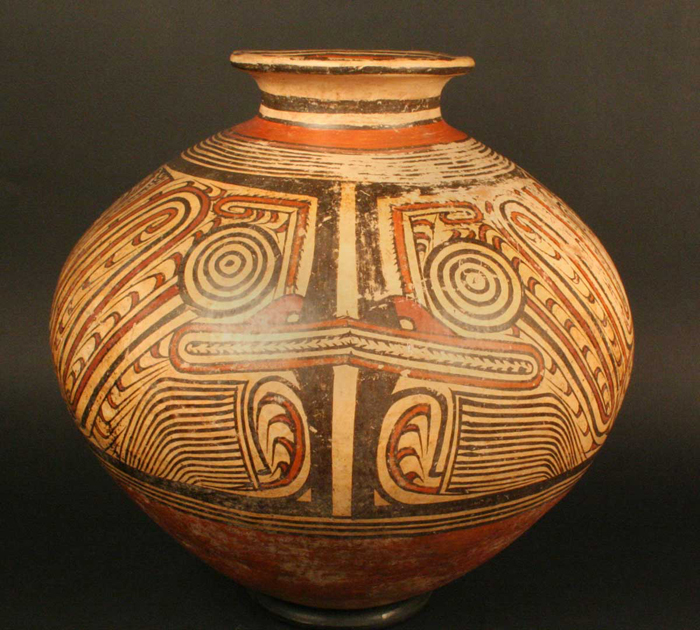
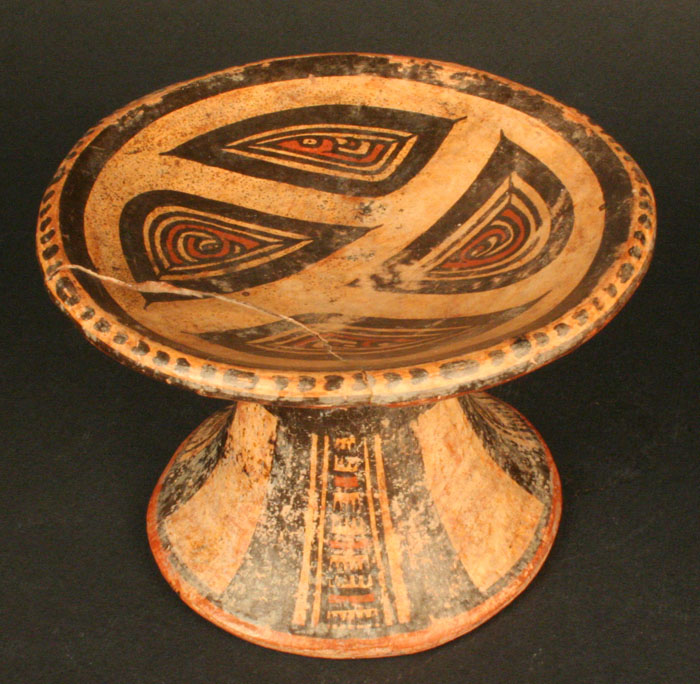
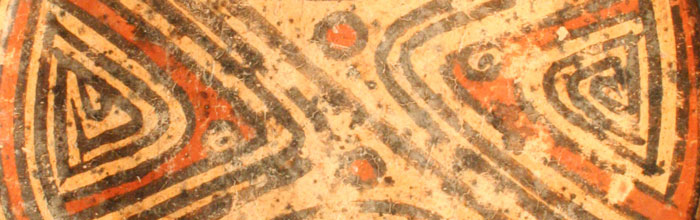
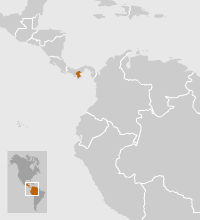
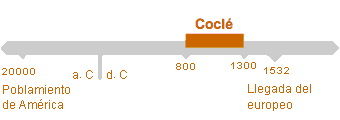This culture emerged in what is now the Panamanian province of Coclé, near the Santa Marta River. The region is warm and humid, with clearly defined seasons. Its landscape includes valleys suitable for agriculture as well as rivers, and woodlands. It is populated by a wide variety of fauna including deer, jaguars, peccaries, coatis, armadillos, and reptiles such as snakes and tortoises, particularly near the coast.
How to Arrive
El Museo se encuentra ubicado en pleno centro de Santiago, en la esquina de las calles Bandera y Compañía, a una cuadra de la Plaza de Armas.
Tickets
Chileans and resident foreigners: $1,000 Foreigners: $8,000 Chilean students and resident foreigners: $500 Foreign students: $4,000
Guided Visit
El Museo cuenta con un servicio de guías, sin costo adicional, para los establecimientos educacionales.
Information for Teachers
Invitamos especialmente a coordinarse con alguno de nuestros guías para programar una visita o actividades de motivación y seguimiento que aprovechen de la mejor forma la experiencia de visitarnos.
Audioguides
Download recordings of the Permanent Exhibition display texts in English, French, Portuguese and Spanish here. These audioguides are in mp3 format and are arranged by cultural area, following the same order as our exhibit galleries. Descargue desde esta página audioguías en castellano, inglés, francés y portugués con los textos de las vitrinas de la […]